 Geo
Geo
提示
Geographic location query, identical to the function provided by Es officially, supports 4 types of geographic location query:
- GeoBoundingBox
- GeoDistance
- GeoPolygon
- GeoShape GeoShape :::
With these 4 types of queries, various powerful and useful functions can be implemented
Application Scenario
- Takeout APP Nearby stores
- Social App Nearby people
- Taxi App Nearby drivers
- Regional crowd portraits APP Extraction of crowd features within a specified range
- Health code, etc.
- ...
EE supports 100% coverage of ES geolocation-related features, and is much easier to use.
Caution
- you need to create or update the indexes before using the geolocation query API
- The first three types of APIs (GeoBoundingBox, GeoDistance, GeoPolygon) must be indexed as geo_point.
- GeoShape field index type must be geo_shape, otherwise the function will not work properly, please refer to the following chart
- field type is recommended to use String, because wkt text format is String, very convenient, as for the field name, see the name to know the meaning.
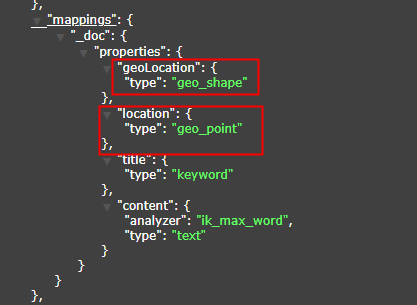
public class Document {
// Omit other fields...
@IndexField(fieldType = FieldType.GEO_POINT)
private String location;
@IndexField(fieldType = FieldType.GEO_SHAPE)
private String geoLocation;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 数据录入
数据插入es方法非常多,这里仅介绍如何使用EE开箱即用API将地理位置数据插入es
@Test
public void testInsert() {
// 省略其它无关字段...
Document document = new Document();
// GEO POINT
document.setLocation("40.171975,116.587105");
// 上面也可以写为下面这样,效果是一样的:
GeoPoint geoPoint = new GeoPoint(40.171975,116.587105);
document.setLocation(geoPoint.toString());
// GEO SHAPE
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(39.084509D, 41.187328D, 70.610461D, 20.498353D);
document.setGeoLocation(rectangle.toString());
int successCount = documentMapper.insert(document);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
插入的数据必须是String,其格式可以直接是经纬度,也可以先创建具体的GeoPoint或Geometry对象,然后调用它的toString方法将其转换为wkt坐标字符串后再插入, 如果直接插入GeoPoint或Geometry对象,会导致插入失败,提示UnknownSource.
# GeoBoundingBox
GeoBoundingBox: 直译为地理边界盒,由左上点和右下点构成的矩形范围,在此范围内的点均可以被查询出来,实际使用的并不多,可参考下图:
! 1 (opens new window)
# API
// Inside the rectangle
geoBoundingBox(R column, GeoPoint topLeft, GeoPoint bottomRight);
// not in rectangle (supported in version 0.9.7+)
notInGeoBoundingBox(R column, GeoPoint topLeft, GeoPoint bottomRight);
2
3
4
5
# Usage examples
@Test
public void testGeoBoundingBox() {
// Query all points located within the rectangle formed by the coordinates of the top left and bottom right points
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
// Assume the coordinates of the top-left point
GeoPoint leftTop = new GeoPoint(41.187328D, 115.498353D);
// Assume the coordinates of the bottom right point
GeoPoint bottomRight = new GeoPoint(39.084509D, 117.610461D);
wrapper.geoBoundingBox(Document::getLocation, leftTop, bottomRight);
// check all points that are not in this rectangle
// wrapper.notInGeoBoundingBox(Document::getLocation, leftTop, bottomRight);
List<Document> documents = documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
documents.forEach(System.out::println);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Warm tips
- the use of the above example only demonstrates one of them, in fact, the framework of the syntax of coordinate points support a variety of ElasticSearch official data formats are supported, the user can choose the corresponding api according to their own habits for the construction of query parameters:
- GeoPoint: the above demo in the use of latitude and longitude representation
- Latitude and longitude arrays: [116.498353, 40.187328], [116.610461, 40.084509]
- Latitude and longitude strings: "40.187328, 116.498353", "116.610461, 40.084509"
- Latitude/Longitude bounding box WKT: "BBOX (116.498353,116.610461,40.187328,40.084509)"
- Latitude/Longitude GeoHash(hash): "xxx"
Among them, the conversion of latitude and longitude hash can be referred to this website: GeoHash coordinate conversion online (opens new window)
# GeoDistance
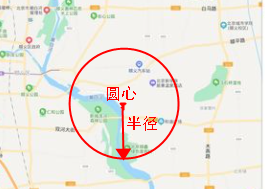
GeoDistance: directly translated as geographic distance, in fact, is a given point as the center of the circle, a given radius to draw a circle, the points in this circle can be found, the use of more high-frequency, such as the take-away software we use to query all the stores around 3 km, you can use this function to achieve, yes you can also be used to write YP software, query the PLMM in the vicinity of three kilometers ...
# API
// Find all points in a circle
geoDistance(R column, Double distance, DistanceUnit distanceUnit, GeoPoint centralGeoPoint);
// check all points that are not in a circle (supported in version 0.9.7+)
notInGeoDistance(R column, Double distance, DistanceUnit distanceUnit, GeoPoint centralGeoPoint);
2
3
4
5
# Usage examples
@Test
public void testGeoDistance() {
// Query all points within a radius of 168.8 kilometers with the latitude 41.0 and the longitude 115.0 as the center.
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
// where the unit can be omitted, the default is km
wrapper.geoDistance(Document::getLocation, 168.8, DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS, new GeoPoint(41.0, 116.0));
// query all points that are not within the circle
// wrapper.notInGeoDistance(Document::getLocation, 168.8, DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS, new GeoPoint(41.0, 116.0));
// The above syntax can also be written in the following forms, the effect is the same, just compatible with different user habits:
// wrapper.geoDistance(Document::getLocation, "1.5km",new GeoPoint(41.0,115.0));
// wrapper.geoDistance(Document::getLocation, "1.5km", "41.0,115.0");
List<Document> documents = documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
System.out.println(documents);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Warm tips
- the same for the coordinate point expression form also support a variety of, and GeoBondingBox in the Tips introduced the same, here will not repeat.
- for the spoiled EE, compatible with a variety of different user habits is a matter of course, so you will find a large number of method overloads, choose one of the most consistent with your habits or to meet the specified use of the api to call the scene.
# GeoPolygon
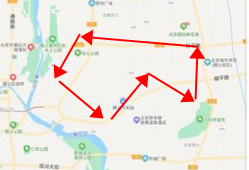
GeoPolygon: the direct translation of the geographic polygon, is actually given all the points of the polygon as a range, query all the points within this range, this function is often used to do electronic fencing, the use of high frequency, such as shared bicycle can be parked area can be achieved through this technology, see the figure below:
# API
geoPolygon(R column, List<GeoPoint> geoPoints)
# Usage examples
@Test
public void testGeoPolygon() {
// Query all points within an irregular graph composed of the given list of points, with at least 3 points
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
List<GeoPoint> geoPoints = new ArrayList<>();
GeoPoint geoPoint = new GeoPoint(40.178012, 116.577188);
GeoPoint geoPoint1 = new GeoPoint(40.169329, 116.586315);
GeoPoint geoPoint2 = new GeoPoint(40.178288, 116.591813);
geoPoints.add(geoPoint);
geoPoints.add(geoPoint1);
geoPoints.add(geoPoint2);
wrapper.geoPolygon(Document::getLocation, geoPoints);
List<Document> documents = documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
System.out.println(documents);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Warm tips
- the same, about the coordinate points of the form of reference, also support a variety of, with the official, you can refer to the GeoBoundingBox in the Tips, here do not repeat. It is worth noting that the number of polygon points can not be less than 3, otherwise Es can not outline the polygon, the query will report an error.
- The index type and field type are the same as the tips in GeoBondingBox
# GeoShape
GeoShape: directly translated as GeoGraph, how to understand? At first glance it seems to be similar to GeoPolygon, but in fact, the previous three types of queries are coordinate points, while this method queries the graphics, such as a park, from the world map can be seen as a point, but if put large enough, such as the map specifically to Hangzhou Binjiang District, the park may become a number of points to form a region, in some special scenarios, you need to In some special scenarios, you need to query the complete region, as well as the intersection of two regions and so on, you need to use GeoShape, if you do not understand, you may wish to read on, to Hangzhou, for example, I give an example of health code, assuming that the black circle in the region for the risk area, I now want to find out all the people in the ES in the Civic Center and in the risk area, their health codes are all turned into orange, that In fact, what I am looking for is the orange area in the figure below, and the area formed by the red arrow is the whole civic center.
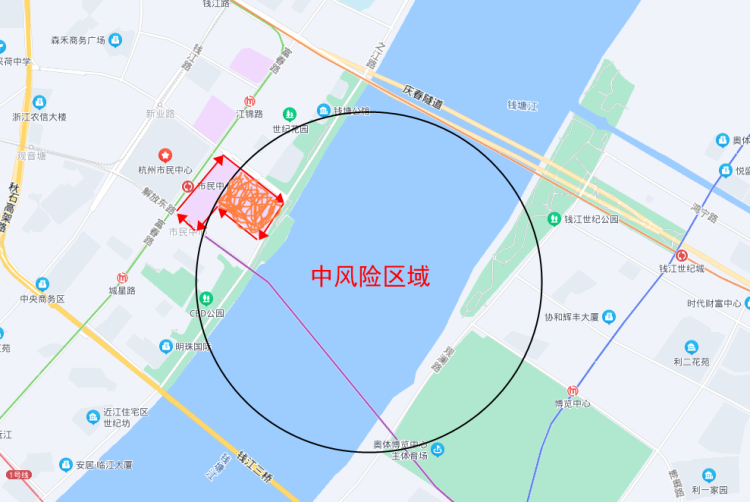
The corresponding ShapeRelation above is INTERSECTS, see the following API.
# API
// Query for shapes that match the indexed shapes
geoShape(R column, String indexedShapeId);
// Query for shapes that do not match the indexed shape (supported in version 0.9.7+)
notInGeoShape(R column, String indexedShapeId);
// Query the list of shapes that match the specified shape and shape relationship
geoShape(R column, Geometry geometry, ShapeRelation shapeRelation);
// query the list of shapes that do not match the specified shape and shape relationship
notInGeoShape(R column, Geometry geometry, ShapeRelation shapeRelation);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Usage examples
This API is not commonly used, or you can skip it and look at the following query by graph.
/**
* Known graph index ID (not commonly used)
* In some high-frequency scenarios, such as a park that has been built, its graphics coordinates are fixed, so you can first save this fixed graphics first into es
* Later you can query directly according to the id of this graph, which is more convenient, so there is this method, but it is not flexible enough and not commonly used
*/
@Test
public void testGeoShapeWithShapeId() {
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
// The indexedShapeId here is the id of the shape that the user has created in Es beforehand
wrapper.geoShape(Document::getGeoLocation, "edu");
// not in case of non-compliance
// wrapper.notInGeoShape(Document::getGeoLocation, "edu");
List<Document> documents = documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
System.out.println(documents);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
This API is more commonly used than the above, i.e., the user can specify whether the graphic to be queried is a rectangle, a circle, or a polygon... (see comments in the code):
/**
* graphics by the user to customize (commonly used), the framework supports Es all supported graphics :
* (Point,MultiPoint,Line,MultiLine,Circle,LineaRing,Polygon,MultiPolygon,Rectangle)
*/
@Test
public void testGeoShape() {
// Note that the query is for a graph, so the index type of the graph field must be geoShape, not geoPoint, so the geoLocation field is used here instead of the location field
LambdaEsQueryWrapper<Document> wrapper = new LambdaEsQueryWrapper<>();
// Here is an example of a circle, where x, y are the coordinates of the center of the circle and r is the radius. Other graphics, please demonstrate the reader to demonstrate, space reasons not one by one to demonstrate
Circle circle = new Circle(13,14,100);
// shapeRelation supports multiple, if not passed then default to within
wrapper.geoShape(Document::getGeoLocation, circle, ShapeRelation.INTERSECTS);
// not in case of non-conformity
// wrapper.notInGeoShape(Document::getGeoLocation, circle, ShapeRelation.INTERSECTS);
List<Document> documents = documentMapper.selectList(wrapper);
System.out.println(documents);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
The above map of the WKT (Well-Known Text) coordinates of the citizen center (polygon) (simulated data, real data can be obtained from Gaode Map/Baidu Map etc. by calling their open APIs):
"POLYGON((108.36549282073975 22.797566864832092,108.35974216461182 22.786093175673713,108.37265968322754 22.775963875498206, 108.4035587310791 22.77600344454008,108.41003894805907 22.787557113881462,108.39557647705077 22.805360509802284,108.36549282073975 22.797566864832092))";
has been stored in Es, in fact, we will be in the project may use the data or business data are stored in Es in advance, otherwise the query will be meaningless, check the air? So the above API according to GeoShape query, you need to pass in the parameters of the range of graphics (the above parameter is a circle).
Warm Tips
GeoShape is easy to confuse with GeoPolygon, need to pay special attention to them, they are actually two different things, the index type also need to be different, the former is geo_point, the latter is geo_shape.
