 Avoid pit
Avoid pit
提示
As the old saying goes, "If you want to be good at what you do, you have to be good at what you do", and "A sharpened knife never fails to cut wood"...
ES itself is huge and complex, the developer has very high requirements, usually senior developers to master, but Easy-Es users are not lack of some ES white or just starting JAVA beginners, in order to make this part to avoid stepping on the pit, To save more time, here is a summary of a guide to avoid the pit, in the formal use of EE before, may spend three or five minutes to learn, you can help you to avoid stepping in the use of the pit, thus saving a lot of time.
When you encounter a problem, try to start from the perspective of whether the use of the standard, version is compatible to start, we have provided the API are covered by test cases, single test coverage rate of up to 95% +, and a large number of community users and production environment to prove that there is no defect, do not do Keyboard warriors, sprayers, up to feel that the framework is full of bugs, a variety of spray, in fact, is their own dish of stubborn feet ... Either do not read the documentation blind j * with, or ES foundation is too poor to step on the ES pit. This type of user actually does not help their technical growth at all, The correct posture should be used according to the documentation specifications, and encounter problems first debug, look at the source code, ask the mother of many ways, really can not solve, you can join our Q&A group, we will help to solve, confirmed as a defect, Block level defects we We will fix it within 24H, other level defects, we will immediately give a solution and circumvent the program, and as soon as possible to issue a version to fix.
# ES version and SpringBoot version
Because we use the ES official underlying RestHighLevelClient, so the ES version requirements, the ES and RestHighLevelClient JAR dependency version must be 7.14.0, as for the es client, the actual X any version can be very good compatibility.
It is worth noting that due to the existence of SpringData-ElasticSearch, Springboot has built-in and ES and RestHighLevelClient dependency versions, which results in different versions of Springboot actually introducing different versions of ES and RestHighLevelClient. versions are different, and the official ES dependencies are very poorly compatible between versions, which further leads to many users not being able to use Easy-Es properly, complaining that our framework is flawed, which is actually just a dependency conflict problem. We did a dependency check at project startup, if your project at startup you can see in the console to print out the level of Error and the content of "Easy-Es supported elasticsearch and restHighLevelClient jar version is: 7.14.0 ,Please resolve the dependency conflict!" When the log is "Easy-Es supported elasticsearch and restHighLevelClient jar version is: 7.14.0 ,Please resolve the dependency conflict! The solution is actually very simple, you can configure the maven exclude like the following to remove Springboot or Easy-Es has been declared ES and RestHighLevelClient dependencies, and then re-introduce, when introduced specify the version number for 7.14.0 can be solved.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.14.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>7.14.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>7.14.0</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
If you're a lazy person, you can simply tweak the springboot version to 2.5.5 and leave everything else untweaked, and it will work just fine.
In addition, if you encounter problems in the use of the process, you may first from the Q & A in search of answers, if you do not find the answers you expect, you can also download our source code, from the test module to find all package, the test class in the package contains almost all the core functions of easy-es, you can refer to. If you still can't solve it, you can join our Q&A group through our community discussion on the website, we will arrange someone to help you for free, but try not to ask some 100,000 questions, everyone's time is very valuable, and our resources are very limited!
# ES index keyword type and text type and termQuery, match, match_phrase difference

If you already know the ES index type and the above query API, you can skip this paragraph.
When we need to do exact match, left fuzzy, right fuzzy, full fuzzy, sorting and aggregation on a query field, we need the index type of the field to be keyword type, otherwise you will find that the query does not find the desired result, or even report an error. For example, the common EE API eq(), like(), distingu(), etc. all require the field type to be keyword type.
When we need to query a field for a word, we need the field type to be text type and specify the word splitter (if you don't specify, you can use the ES default word splitter, which is usually not ideal). For example, the API match(), which is commonly used in EE, requires the field type to be text type. When using match query does not query the expected results, you can first check the index type, and then check the separator, because if a word is not separated out by the separator, the results are also not queried.
When the same field, we need to use it both as a keyword type, but also need to use it as a text type, then our index type for the keyword_text type, EE does not specify the field type, the default field type for this keyword + text double type, double type as shown below, it is worth noting that when we put the field keyword type query, ES requires that the field name passed in is called "field name.keyword", when the field when the text type query, the original field name can be used directly. Thankfully, since version 2.0, the framework has been handled internally, the default will be based on the current field index type and the type of query to determine the actual use of which type, .keyword suffix framework will be automatically spliced to further reduce the possibility of the white man stepped on this pit, if you do not want the framework automatically spliced according to the context .keyword suffix, you can also be used through the configuration file to turn off this intelligent feature, easy-es.global-config.db-config.smartAddKeywordSuffix=false
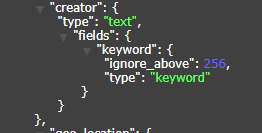
# Field id
Since many functions of the framework are implemented with the help of ids, such as selectById, update, deleteById... , and ES must also have a column as data id, so we force the user to package the entity class contains field id column, otherwise the framework can not be used properly many functions.
public class Document {
/**
* Recommended method 1: Unique id in es, without any annotation or @IndexId(type=IdType.NONE). At this time, the id value will be automatically generated by es
*/
private String id;
/**
* Not recommended method 2: If you want to customize the id provided for you by the id in es, such as the id in MySQL, please specify the type in the annotation as customize or directly specify it in the global configuration file, then you can Assign value to id when inserting data
*/
@IndexId(type = IdType.CUSTOMIZE)
private Long id;
/**
* Recommended method 3: If you really need to use the IDs in other databases, you might as well add the ID in recommended method 1 and add a column with a field type of keyword to store the IDs in other databases.
*/
@IndexField(fieldType = FieldType.KEYWORD)
private Long mysqlId;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
It is strongly recommended to use the recommended method. Just add a line of private String id directly to the entity class. Don't add any superfluous information. If you really want to retrieve the id of the corresponding data in the MySQL library in ES, you might as well add a new column and write it according to recommended method 3. Because if you forcibly use the id generated by mysql or other algorithms as the _id of es, when inserting data, es will calculate whether the id is unique on all shards. This process will affect the service as the amount of data increases. fatal effects, And it is strongly recommended not to use ES's _id for sorting. This will also easily lead to OOM. For similar reasons, ES officials do not recommend you to do this, but you can add a new row of keyword type index fields like recommended method 3, such as mysqlId. , Use this new field to perform various operations such as CRUD and sorting. At this time, the performance will not be affected. In short, remember that the ID is generated by es itself. It is not recommended to play tricks by yourself.
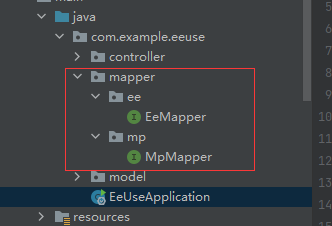
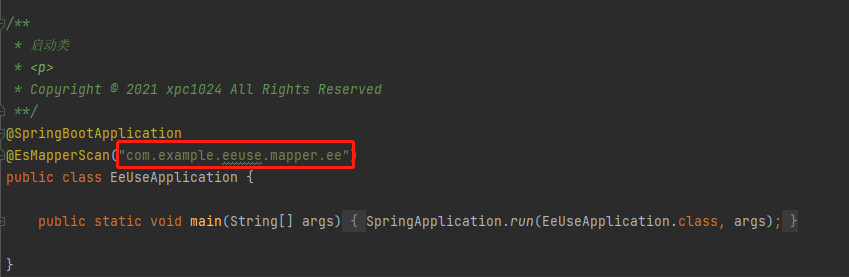
# Using Mybatis-Plus and Easy-Es in your project at the same time
In this scenario, you need to put the MP mapper and EE mapper in different directories and configure the scan path with their respective scan paths, so that they can coexist, otherwise both start in SpringBoot to scan the same path and try to register as their own beans, because the underlying implementation depends on a completely different class, so it will lead to one of the registration failure, the entire project can not start properly. You can refer to the following diagram:
I wish you all a happy use, use any questions and suggestions, you can add my WeChat 252645816 feedback, we also have a special Q&A group to provide free service for all the masters.
